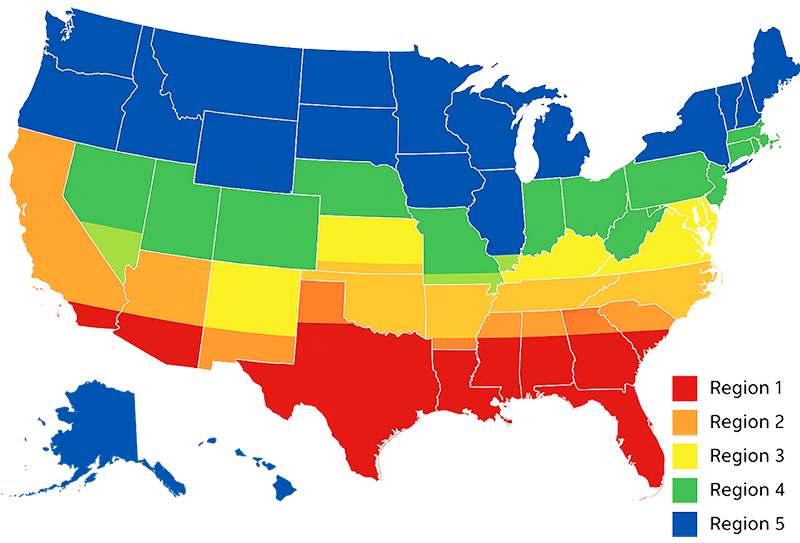
- System tonnage
AC Tonnage and BTU Calculator
-


Our price:
$2,648.00Sale price:
$2,070.00List price:
$3,202.00Our price:
$2,648.00You save: 22% ($1,132.00)

Our price:
$2,818.00Sale price:
$2,170.00List price:
$3,392.00Our price:
$2,818.00You save: 23% ($1,222.00)

List price:
$4,009.00Our price:
$2,315.00You save $1,694.00!

Our price:
$2,435.00Sale price:
$2,330.00List price:
$3,050.00Our price:
$2,435.00You save: 4% ($720.00)

Our price:
$3,206.00Sale price:
$2,335.00List price:
$3,830.00Our price:
$3,206.00You save: 27% ($1,495.00)

Our price:
$3,107.00Sale price:
$2,335.00List price:
$3,699.00Our price:
$3,107.00You save: 25% ($1,364.00)

Our price:
$2,716.00Sale price:
$2,399.00List price:
$3,174.00Our price:
$2,716.00You save: 12% ($775.00)

Our price:
$3,347.00Sale price:
$2,399.00List price:
$4,009.00Our price:
$3,347.00You save: 28% ($1,610.00)

Our price:
$3,266.00Sale price:
$2,415.00List price:
$3,535.00Our price:
$3,266.00You save: 26% ($1,120.00)

Our price:
$2,854.00Sale price:
$2,480.00List price:
$3,238.00Our price:
$2,854.00You save: 13% ($758.00)

Our price:
$3,489.00Sale price:
$2,480.00List price:
$4,137.00Our price:
$3,489.00You save: 29% ($1,657.00)

Our price:
$3,296.00Sale price:
$2,480.00List price:
$3,939.00Our price:
$3,296.00You save: 25% ($1,459.00)

Our price:
$2,966.00Sale price:
$2,540.00List price:
$3,300.00Our price:
$2,966.00You save: 14% ($760.00)

List price:
$3,224.00Our price:
$2,550.00You save $674.00!

List price:
$3,846.00Our price:
$2,550.00You save $1,296.00!

Our price:
$3,193.00Sale price:
$2,580.00List price:
$3,381.00Our price:
$3,193.00You save: 19% ($801.00)

List price:
$3,711.00Our price:
$2,590.00You save $1,121.00!

Our price:
$3,626.00Sale price:
$2,595.00List price:
$3,980.00Our price:
$3,626.00You save: 28% ($1,385.00)

List price:
$3,925.00Our price:
$2,655.00You save $1,270.00!

Our price:
$3,273.00Sale price:
$2,675.00List price:
$3,585.00Our price:
$3,273.00You save: 18% ($910.00)

Our price:
$3,622.00Sale price:
$2,680.00List price:
$4,416.00Our price:
$3,622.00You save: 26% ($1,736.00)

Our price:
$3,867.00Sale price:
$2,685.00List price:
$4,792.00Our price:
$3,867.00You save: 31% ($2,107.00)

Our price:
$3,543.00Sale price:
$2,715.00List price:
$3,930.00Our price:
$3,543.00You save: 23% ($1,215.00)

Our price:
$3,696.00Sale price:
$2,715.00List price:
$4,473.00Our price:
$3,696.00You save: 27% ($1,758.00)

Our price:
$3,924.00Sale price:
$2,755.00List price:
$4,580.00Our price:
$3,924.00You save: 30% ($1,825.00)

List price:
$4,121.00Our price:
$2,780.00You save $1,341.00!

Our price:
$3,468.00Sale price:
$2,790.00List price:
$3,643.00Our price:
$3,468.00You save: 20% ($853.00)

Our price:
$3,708.00Sale price:
$2,799.00List price:
$3,940.00Our price:
$3,708.00You save: 25% ($1,141.00)

List price:
$4,457.00Our price:
$2,799.00You save $1,658.00!

List price:
$4,216.00Our price:
$2,815.00You save $1,401.00!

Our price:
$4,102.00Sale price:
$2,850.00List price:
$4,758.00Our price:
$4,102.00You save: 31% ($1,908.00)

Our price:
$3,734.00Sale price:
$2,860.00List price:
$3,812.00Our price:
$3,734.00You save: 23% ($952.00)

Our price:
$4,214.00Sale price:
$2,860.00List price:
$5,046.00Our price:
$4,214.00You save: 32% ($2,186.00)

Our price:
$3,326.00Sale price:
$2,895.00List price:
$4,319.00Our price:
$3,326.00You save: 13% ($1,424.00)

Our price:
$3,869.00Sale price:
$2,895.00List price:
$4,165.00Our price:
$3,869.00You save: 25% ($1,270.00)

Our price:
$3,355.00Sale price:
$2,910.00List price:
$4,342.00Our price:
$3,355.00You save: 13% ($1,432.00)

List price:
$4,637.00Our price:
$2,920.00You save $1,717.00!

List price:
$4,714.00Our price:
$2,925.00You save $1,789.00!

Our price:
$3,520.00Sale price:
$2,945.00List price:
$3,978.00Our price:
$3,520.00You save: 16% ($1,033.00)

List price:
$3,939.00Our price:
$2,955.00You save $984.00!

Our price:
$3,331.00Sale price:
$2,965.00List price:
$3,855.00Our price:
$3,331.00You save: 11% ($890.00)

Our price:
$4,280.00Sale price:
$2,995.00List price:
$4,280.00Our price:
$4,280.00You save: 30% ($1,285.00)

Our price:
$4,470.00Sale price:
$2,995.00List price:
$5,492.00Our price:
$4,470.00You save: 33% ($2,497.00)

Our price:
$3,642.00Sale price:
$3,035.00List price:
$4,099.00Our price:
$3,642.00You save: 17% ($1,064.00)

List price:
$3,936.00Our price:
$3,035.00You save $901.00!

Our price:
$3,398.00Sale price:
$3,045.00List price:
$3,960.00Our price:
$3,398.00You save: 10% ($915.00)

Our price:
$4,296.00Sale price:
$3,050.00List price:
$5,062.00Our price:
$4,296.00You save: 29% ($2,012.00)

Our price:
$3,953.00Sale price:
$3,060.00List price:
$3,953.00Our price:
$3,953.00You save: 23% ($893.00)

Our price:
$3,428.00Sale price:
$3,065.00List price:
$3,985.00Our price:
$3,428.00You save: 11% ($920.00)

List price:
$4,182.00Our price:
$3,075.00You save $1,107.00!

List price:
$4,959.00Our price:
$3,075.00You save $1,884.00!

Our price:
$3,686.00Sale price:
$3,085.00List price:
$4,162.00Our price:
$3,686.00You save: 16% ($1,077.00)

List price:
$4,106.00Our price:
$3,085.00You save $1,021.00!

List price:
$4,908.00Our price:
$3,095.00You save $1,813.00!

Our price:
$3,783.00Sale price:
$3,110.00List price:
$4,196.00Our price:
$3,783.00You save: 18% ($1,086.00)

Our price:
$4,294.00Sale price:
$3,135.00List price:
$4,575.00Our price:
$4,294.00You save: 27% ($1,440.00)

Our price:
$3,827.00Sale price:
$3,155.00List price:
$4,258.00Our price:
$3,827.00You save: 18% ($1,103.00)

Our price:
$3,960.00Sale price:
$3,185.00List price:
$4,303.00Our price:
$3,960.00You save: 20% ($1,118.00)

Our price:
$4,618.00Sale price:
$3,195.00List price:
$5,241.00Our price:
$4,618.00You save: 31% ($2,046.00)

Our price:
$3,835.00Sale price:
$3,195.00List price:
$4,744.00Our price:
$3,835.00You save: 17% ($1,549.00)

Our price:
$3,863.00Sale price:
$3,205.00List price:
$3,950.00Our price:
$3,863.00You save: 17% ($745.00)

Our price:
$4,384.00Sale price:
$3,215.00List price:
$4,384.00Our price:
$4,384.00You save: 27% ($1,169.00)

Our price:
$3,983.00Sale price:
$3,220.00List price:
$4,349.00Our price:
$3,983.00You save: 19% ($1,129.00)

Our price:
$4,034.00Sale price:
$3,225.00List price:
$4,355.00Our price:
$4,034.00You save: 20% ($1,130.00)

List price:
$4,271.00Our price:
$3,235.00You save $1,036.00!

List price:
$4,748.00Our price:
$3,240.00You save $1,508.00!

List price:
$5,304.00Our price:
$3,245.00You save $2,059.00!

Our price:
$4,675.00Sale price:
$3,250.00List price:
$4,925.00Our price:
$4,675.00You save: 30% ($1,675.00)

Our price:
$4,058.00Sale price:
$3,255.00List price:
$4,392.00Our price:
$4,058.00You save: 20% ($1,137.00)

List price:
$5,501.00Our price:
$3,260.00You save $2,241.00!

Our price:
$4,040.00Sale price:
$3,275.00List price:
$4,419.00Our price:
$4,040.00You save: 19% ($1,144.00)

List price:
$4,238.00Our price:
$3,285.00You save $953.00!

Our price:
$4,132.00Sale price:
$3,290.00List price:
$4,444.00Our price:
$4,132.00You save: 20% ($1,154.00)

List price:
$4,315.00Our price:
$3,295.00You save $1,020.00!

List price:
$4,694.00Our price:
$3,295.00You save $1,399.00!