High-Tech HVAC Tools: Why This Guide Matters to Pros
This guide is written for working pros in residential and light-commercial HVAC who already speak Manual J, S, and D, follow manufacturer specifications, and work to code. We focus on how modern instruments, software, and workflows sharpen the core practices you already rely on. By high-tech HVAC tools, we mean digital measurement devices, connected sensors and probes, mobile apps, and cloud-backed platforms that capture data, analyze it, and document results for design, installation, commissioning, and service.
Think of it like moving from a tape measure to a laser level: the readings come faster and with tighter repeatability, but you still need to know where to place the target. Fundamentals stay in the driver's seat, and technology enforces them with real-time feedback, trend data, and standardized processes. Used that way, tools do more than speed you up. They reduce guesswork, align field work with load calculations and duct design, validate equipment setup against manufacturer tables, and create records that stand up to inspection and callbacks. Pairing tech with sound fundamentals is what turns a capable technician into a high-performing specialist.
Why High-Tech Tools Matter: Faster Diagnosis, Better Outcomes, Higher Profits
After decades on rooftops and in mechanical rooms, we have learned that high-tech tools turn HVAC work from feel into facts. Data-driven design and commissioning, using load-calculation and duct-design apps with Manual J, S and D integration, plus airflow measurement, lets technicians size, balance and commission systems correctly. That avoids oversizing, starved returns and hot or cold rooms, and helps hit manufacturer static pressure and CFM targets on day one.
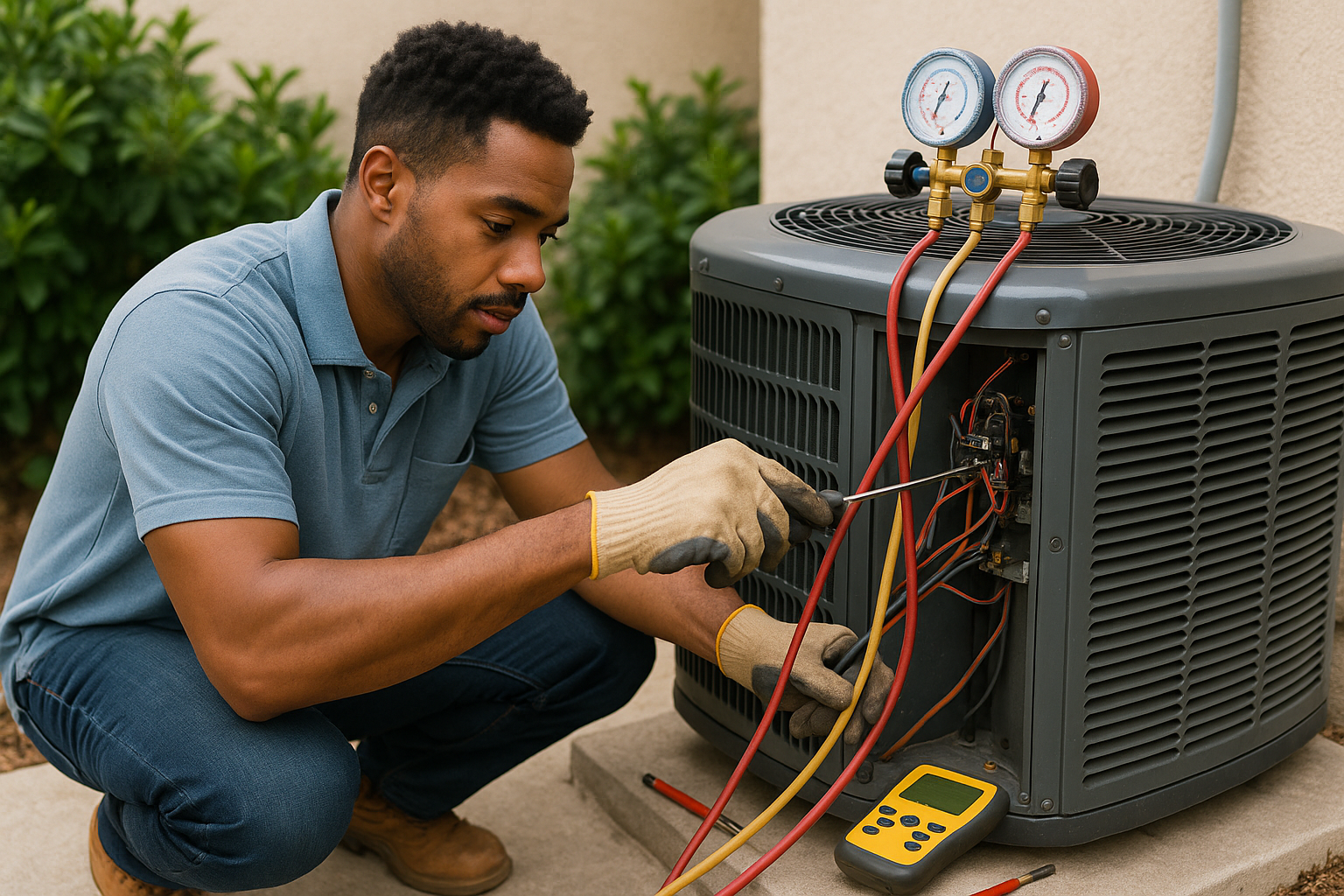
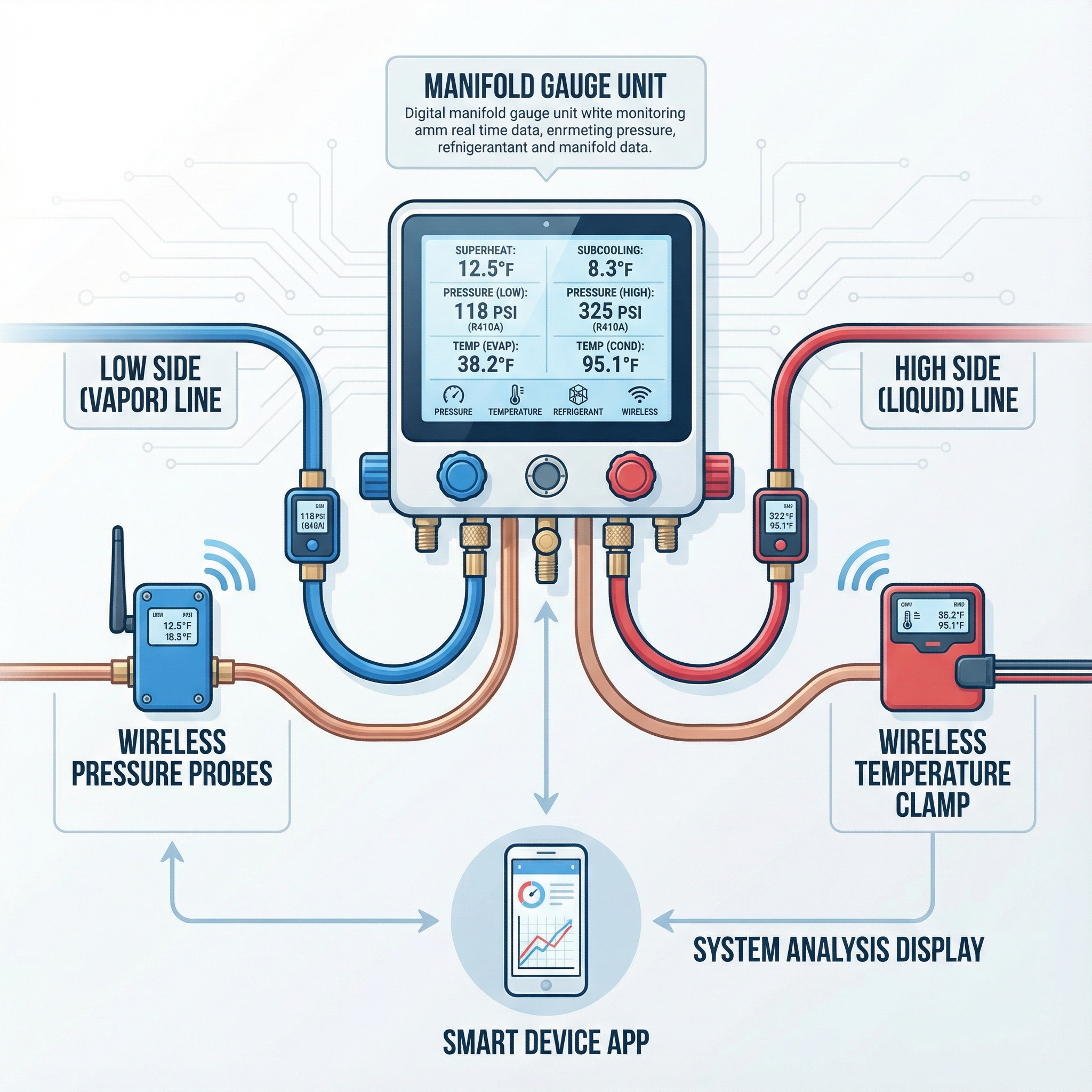
Precision diagnostics beats guesswork. Digital manifolds, wireless temperature and pressure probes, and advanced leak detectors provide live superheat, subcool and delta T, so charge, airflow and system health can be verified quickly. It is like a doctor reading an ECG instead of relying on a pulse, the signal is clear, repeatable and documented.
- Faster diagnosis, less time onsite and more first-visit fixes.
- Fewer callbacks because faults are measured, not assumed.
- Documented performance, before and after data the customer can understand.
- Higher profitability through accurate repairs and efficient commissioning.
Technicians who master these tools can show measurable improvements, such as total external static pressure, delivered CFM per ton and room-by-room balance. That transparency differentiates service, supports verifiable comfort and efficiency gains, and builds lasting trust in the quality of the work.
Regional & Regulatory Context: How Climate, Codes and Refrigerant Rules Shape Tool Needs
Climate is like the job site itself, it sets the ground rules. In hot-dry regions, techs chase sensible load and airflow, so precise static pressure probes and data logging help confirm high SEER performance while keeping humidity in check. In hot-humid areas, the emphasis shifts to latent removal: hygrometers, psychrometric apps and airflow balancing verify dehumidification and filtration targets. Mixed-humid markets reward correct sizing and zoning, backed by Manual J, S and D with local climate data and IAQ goals.
Codes tighten the screws on verification. The DOE's SEER2, EER2 and HSPF2 regime took effect Jan 1, 2023, with regional minimums around 13.4 SEER2 in the north and 14.3 SEER2 in the south. Many jurisdictions also adopt or exceed federal baselines, adding duct sealing, ventilation and commissioning requirements. High-tech HVAC tools are essential to validate SEER2/HSPF2 compliance, capture commissioning data and produce records customers and inspectors accept. In our experience at Budget Heating (BudgetHeating.com), time-stamped photos, sensor logs and clear reports reduce callbacks and streamline warranty or code paperwork.
Refrigerant policy is reshaping field practice. A2L-related safety standards, including ASHRAE 15/34 and UL 60335-2-40, are being written into updated mechanical and electrical codes. The EPA AIM Act begins technology transitions in 2026 with lower GWP refrigerants and sell-through limits, which means new handling expectations. That makes leak detection, ventilation checks and proper pressure testing nonnegotiable, and documenting CO readings and safety checks creates defensible records that protect both the customer and the technician. Noninvasive tools like thermal imagers, borescopes and wireless sensors also let teams inspect with minimal disruption, a win for homeowners and facility managers.
Thermal Imaging Cameras: How Pros Spot Problems Hidden to the Eye
Thermal imagers read infrared and translate it into a color map, like a weather radar for temperature. We look for patterns: blotchy cold patches in ceilings point to missing insulation, thin cool streaks tracing duct runs signal leakage at joints, and straight cool lines across walls mark thermal bridging at studs or headers. On equipment, a motor with a failing bearing shows a small concentrated hot ring at the end bell. Refrigerant issues show as uneven coil temps, a very cold suction line near the air handler, or a warm liquid line. Beyond being noninvasive, the real value comes when we pair the imager with data: temperature and humidity logging, IAQ sensors for CO2 or VOCs, and refrigerant pressure and temperature readings to verify superheat and subcool and guide ventilation and comfort fixes. That combination confirms root causes instead of chasing symptoms.
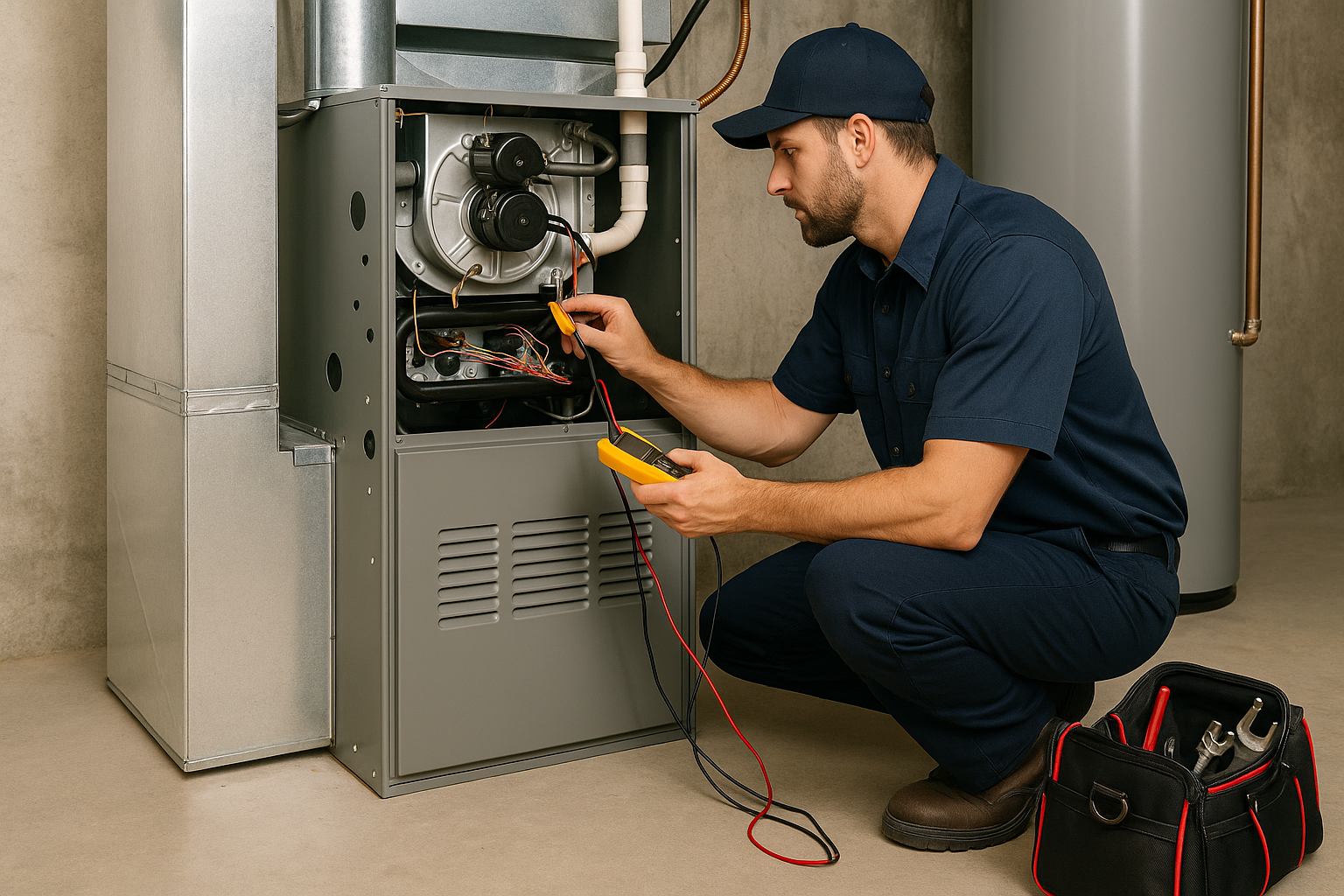
Combustion Analyzers & CO Monitors: Safety First on Furnaces and Boilers
Combustion testing is not guesswork. We start with lockout/tagout and verify power with properly rated meters, then insert a combustion analyzer probe in the flue. The instrument reads CO, O2, stack temperature, and draft to show how completely fuel is burning. Elevated CO, low O2, or weak draft calls for immediate mitigation: shut the appliance down, ventilate, correct gas pressure, clean burners, check heat exchanger integrity, and resolve venting issues before return to service. Documented readings protect occupants and reduce liability because decisions are based on measured facts, not impressions. The same precision tools streamline seasonal maintenance workflows. Along with coil inspections, blower amperage and static pressure checks, and defrost verification on heat pumps, verified combustion numbers catch problems early, preventing nuisance lockouts and the kind of failure that turns a simple tune up into a costly repair.
Top 10 High-Tech HVAC Tools Pros Never Leave Home Without
Use this quick map by task: diagnostic, charging, safety, airflow, controls, documentation.
- Digital manifold gauges: charging and diagnostics, capture stable pressures, temps, superheat and subcool quickly.
- Wireless refrigerant scale: charging, dial in charge by weight without guesswork.
- Infrared or thermal imager: diagnostics and airflow, spot duct losses, overheated motors, cold spots.
- Ultrasonic or electronic leak detector: diagnostics and safety, pinpoint refrigerant leaks fast.
- Borescope: diagnostics, inspect coils, heat exchangers and drains without teardown.
- Combustion analyzer: safety and tune-up, set gas input, verify O2, CO, draft.
- Blower-door and duct-test rig: airflow, measure building and duct leakage to guide sealing and balancing.
- Clamp meter or multimeter: controls and electrical, verify amps, voltage drop, capacitors and flame-sensor microamps.
- Refrigerant identifier and recovery machine: safety and charging, confirm purity and recover properly.
- Data loggers and mobile apps: documentation and controls, trend temps, humidity and pressures, create shareable reports.
In our experience at Budget Heating (BudgetHeating.com), crews that document findings with logs and photos solve callbacks faster and build trust with customers.
Common Mistakes & Limits: When High-Tech Tools Aren't the Whole Answer
After three decades turning wrenches and commissioning systems, we love smart gauges and apps, yet we also see where tools fall short. Nameplate SEER does not guarantee low bills if the system is mischarged, airflow is off, or ducts leak. Bigger equipment is not better, oversizing leads to short cycling and clammy rooms, which is why proper Manual J sizing matters. A unit that heats or cools may still be unsafe or inefficient, diagnostics are what uncover hidden faults.
Frequent pitfalls: installing without checking current codes and regional efficiency rules, which invites failed inspections and rework. Relying on uncalibrated instruments, which can mislead more than help, set calibration intervals and cross check readings. Believing advanced tools are only for complex jobs, even routine maintenance benefits from data logging, imaging, and digital pressure readings.
Where the tech is not the fix: very cold climates can push heat pumps past their comfort zone, plan for auxiliary heat or a hybrid setup, and improve the building envelope. No tool compensates for poor duct design or leakage, redesign and sealing beat gadgetry. And when budget constraints force corner cutting, fewer high quality steps done right outperform a pile of half measures.
Ultrasonic & Electronic Leak Detectors, and Safe Refrigerant Handling
In our 30+ years working with HVAC tools, we treat leak detection as a safety exercise first. Ultrasonic and electronic detectors fit into this plan, provided they are rated for A2Ls. As jurisdictions move toward low-GWP A2L refrigerants, technicians must use detectors specifically rated for A2Ls, pair them with compatible recovery machines, and follow manufacturer instructions as well as applicable codes. That combination supports safety and compliance.
Practical approach: verify the detector's A2L listing before you start, confirm the recovery equipment is approved for the refrigerant on site, then document the leak location and corrective steps in line with code and the equipment manual. Planning A2L-ready tools now reduces surprises when regulations tighten.

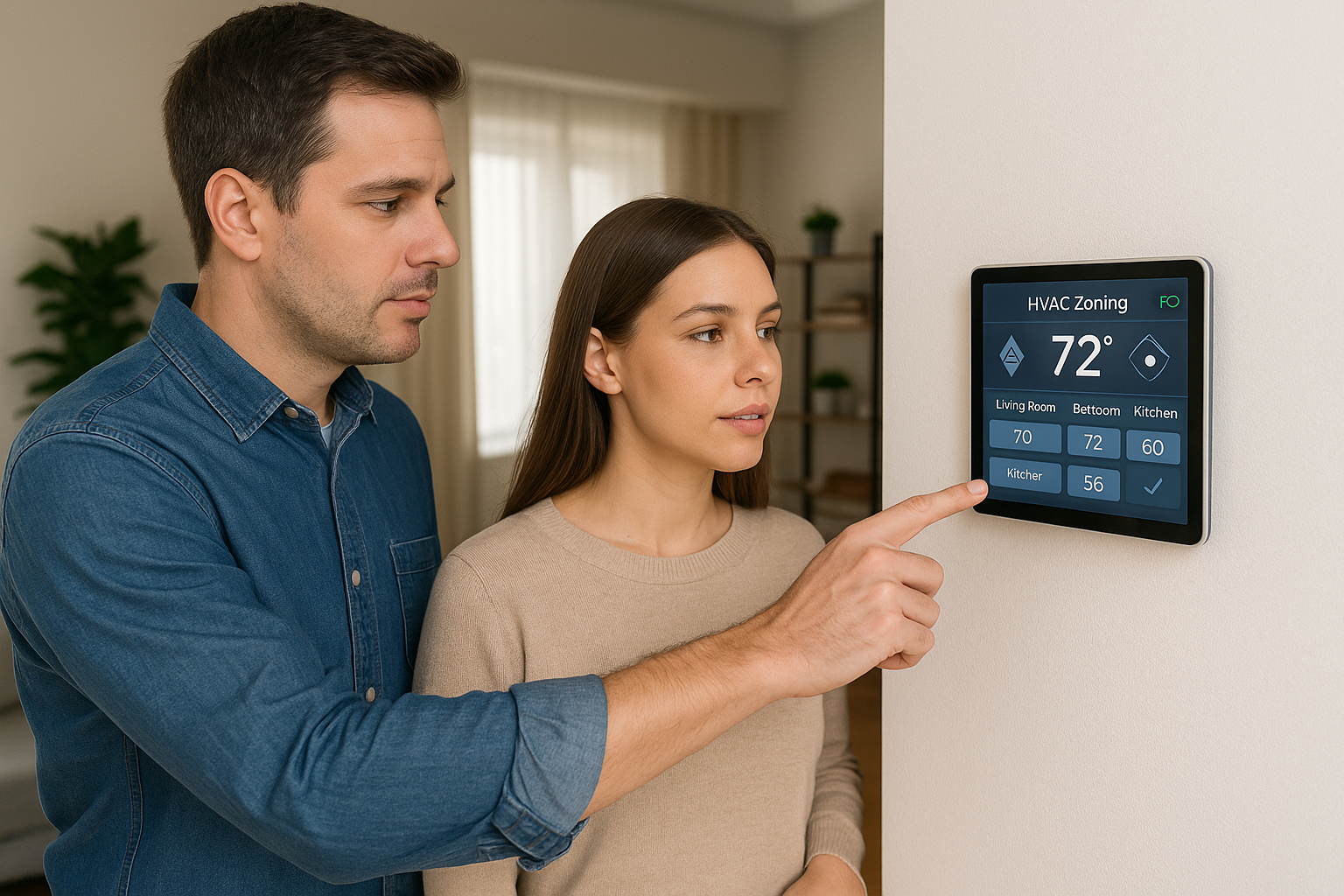
Smart Sensors, IoT Monitoring & Mobile Apps: Remote Diagnostics and Predictive Maintenance
In our field work, smart sensors on temperature, pressure, humidity and power draw feed a secure cloud, giving a live and historical view of system health. Mobile apps and cloud storage keep documentation searchable, which supports long-term trend analysis and clear customer reporting. Think of it as a flight recorder for HVAC, quietly collecting clues every minute.
Time-series data logging lets us spot patterns that are easy to miss on a single visit: seasonal drift in charge, short cycling after thermostat changes, fan runtime creep, or a slow decline in latent capacity. With thresholds and alerts, predictive maintenance becomes practical, so parts get replaced before a breakdown and callbacks drop while equipment life improves.
Smart thermostats and communicating controls also need verification of staging, fan profiles and dehumidification settings. Data logging confirms each stage engages as intended, airflow hits targets and moisture removal tracks setpoints. We compare today's curves to baseline data-driven commissioning to diagnose issues remotely and dispatch accurately.

Conclusion & Next Steps: Equip Your Team, Increase Efficiency, Win More Jobs
Pro results start with disciplined tool care. Calibrate on schedule, keep sensors and filters clean, store tools in cases, and cross-check critical readings with a second method. Treat batteries, probes and filters as consumables, keep firmware and refrigerant knowledge current. Lead with noninvasive diagnostics first. Commission high SEER and SEER2 systems with digital manifolds, wireless probes and airflow diagnostics, then verify blower airflow and static pressure with a manometer. Use Manual J, S and D plus local code to pick the right SEER tier. This workflow documents compliance, supports refrigerant transitions and pays back with fewer callbacks and better records, and it layers cleanly with predictive sensors.
We know choosing tools and workflows can feel complex. Our team, 30+ years in HVAC and factory-authorized, pairs vetted gear with commissioning checklists and U.S.-based phone support so your installs deliver rated performance.
- Get a Custom Quote
- Talk to Our Team
- Shop HVAC Tools
- Financing with Affirm and fast shipping available